Product Description
Product introduction
| Modulo | Above 0.8 |
| Numero di Denti | Above 9teeth |
| Angolo d’Elica Helix Angle | Up to 45 |
| bore diameter | Above 6mm |
| axial length | Above 9mm |
| Gear model | Customized gear accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| Processing machine | CNC machine |
| Material | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA/304 stainless steel |
| Heat treattment | Carburizing and quenching/ Tempering/ Nitriding/ Carbonitriding/ Induction hardening |
| Hardness | 35-64HRC |
| Qaulity standerd | GB/ DIN/ JIS/ AGMA |
| Accuracy class | 5-8 class |
| Shipping | Sea shipping/ Air shipping/ Express |
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
|---|---|
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear/Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Type: | Worm And Wormwheel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
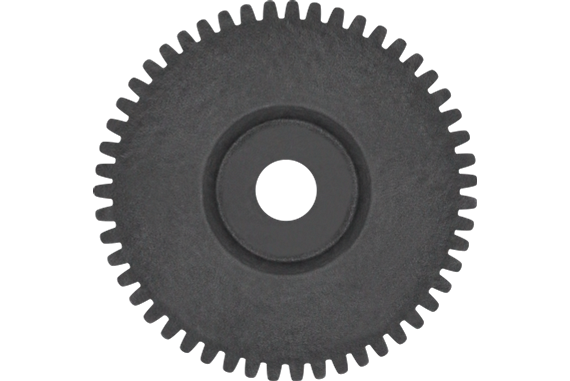
How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with spur gears?
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears involves modifying or replacing certain components to incorporate spur gears into the system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Evaluate the Existing System:
Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to determine its design, function, and limitations. Identify the specific components that need to be retrofitted with spur gears and understand how the system operates.
2. Design Considerations:
Based on the evaluation, consider the design considerations for integrating spur gears into the system. This includes factors such as gear size, tooth profile, gear material, gear ratio, and torque requirements. Determine the specific gear specifications that are compatible with the existing system.
3. Gear Selection:
Select the appropriate spur gears that meet the required specifications. Consider factors such as gear quality, load capacity, noise level, efficiency, and compatibility with the existing system components. Choose gears from reputable manufacturers or consult with a gear specialist for guidance.
4. Gear Positioning and Alignment:
Determine the optimal positioning and alignment of the spur gears within the existing system. This involves identifying the gear locations, shaft connections, and ensuring proper alignment with other components such as bearings and couplings. Accurate positioning and alignment are crucial for efficient gear operation and longevity.
5. Modification or Replacement:
Based on the design considerations and gear selection, proceed with the necessary modifications or replacements. This may involve removing existing components, such as gears with different tooth profiles, and replacing them with the selected spur gears. Ensure proper installation and secure attachment of the new gears.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Implement appropriate lubrication practices for the newly retrofitted spur gears. Consult gear manufacturers’ recommendations for lubricant type, quantity, and maintenance intervals. Proper lubrication ensures smooth gear operation, reduces wear, and extends gear life.
7. Testing and Validation:
After the retrofitting process, conduct thorough testing and validation of the modified system. Verify that the spur gears are functioning as intended, ensuring proper engagement, smooth operation, and adequate load handling. Address any issues or discrepancies discovered during testing.
8. Documentation and Training:
Create documentation detailing the retrofitting process, including gear specifications, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements. This documentation serves as a reference for future maintenance and helps ensure consistent gear performance. Additionally, provide training to relevant personnel on the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the retrofitted system.
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears requires careful planning, proper gear selection, precise installation, and thorough testing. By following these steps and considering the specific requirements of the system, it is possible to successfully incorporate spur gears and enhance the performance and functionality of the mechanical system.

What is the lifespan of a typical spur gear?
The lifespan of a typical spur gear can vary significantly depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The lifespan of a spur gear is influenced by various factors, including:
- Operating Conditions: The conditions under which the spur gear operates greatly impact its lifespan. Factors such as the magnitude and frequency of the applied loads, operating temperature, speed, and lubrication quality play a significant role. Gears operating under heavy loads, high speeds, or harsh environments may experience higher wear and fatigue, potentially reducing their lifespan.
- Material Selection: The material used for constructing the spur gear affects its durability and lifespan. Spur gears are commonly made from materials such as steel, cast iron, bronze, or polymer composites. The specific material properties, including hardness, strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion, influence the gear’s ability to withstand the operating conditions and determine its lifespan.
- Quality of Manufacturing: The quality of manufacturing processes and techniques employed during the production of the spur gear can impact its lifespan. Gears manufactured with precision, accurate tooth profiles, and proper heat treatment are more likely to have longer lifespans compared to those with manufacturing defects or poor quality control.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in spur gears. Regular maintenance practices, including lubricant replacement, gear inspections, and addressing any issues promptly, can significantly extend the lifespan of the gears. Inadequate lubrication or neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear and failure.
- Load and Stress Distribution: The design and configuration of the gear system affect the load and stress distribution on the spur gears. Proper gear design, including tooth profile, number of teeth, and gear arrangement, helps ensure even load distribution and minimizes localized stress concentrations. Well-designed supporting components, such as bearings and shafts, also contribute to the overall lifespan of the gear system.
It is challenging to provide a specific lifespan for a typical spur gear since it depends on the aforementioned factors and the specific application. Spur gears can have lifespans ranging from several thousand to millions of operating cycles. Industrial gear systems often undergo regular inspections and maintenance, including gear replacement when necessary, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
It’s important to note that gear lifespan can be extended through proper care, maintenance, and adherence to recommended operating parameters. Regular inspections, monitoring of gear performance, and addressing any signs of wear or damage promptly can help maximize the lifespan of spur gears.
When assessing the lifespan of spur gears for a particular application, it is advisable to consult manufacturers, industry standards, and experts with expertise in gear design and maintenance for accurate estimations and recommendations.
Are there different sizes and configurations of spur gears available?
Yes, there are various sizes and configurations of spur gears available to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different options when it comes to sizes and configurations of spur gears:
Sizes: Spur gears come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate different torque and speed requirements. The size of a spur gear is typically specified by its pitch diameter, which is the diameter of the pitch circle. The pitch diameter determines the gear’s overall size and the spacing between the teeth. Spur gears can range from small gears used in precision instruments to large gears used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Module: Module is a parameter used to specify the size and spacing of the teeth on a spur gear. It represents the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. Different module sizes are available to accommodate various gear sizes and applications. Smaller module sizes are used for finer tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are used for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a spur gear can vary depending on the specific application. Gears with a higher number of teeth provide smoother operation and distribute the load more evenly, whereas gears with fewer teeth are typically used for higher speeds and compact designs.
Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is an important parameter that determines the shape and engagement of the teeth. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees. The selection of the pressure angle depends on factors such as load capacity, efficiency, and specific design requirements.
Profile Shift: Profile shift is a design feature that allows modification of the tooth profile to optimize the gear’s performance. It involves shifting the tooth profile along the gear’s axis, which can affect factors such as backlash, contact ratio, and load distribution. Profile shift can be positive (when the tooth profile is shifted towards the center of the gear) or negative (when the tooth profile is shifted away from the center).
Hub Configuration: The hub refers to the central part of the gear where it is mounted onto a shaft. Spur gears can have different hub configurations depending on the specific application. Some gears have a simple cylindrical hub, while others may have keyways, set screws, or other features to ensure secure and precise mounting.
Material and Coatings: Spur gears are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions and requirements. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Additionally, gears can be coated or treated with surface treatments such as heat treatment or coatings to enhance their wear resistance, durability, and performance.
Mounting Orientation: Spur gears can be mounted in different orientations depending on the application and space constraints. They can be mounted parallel to each other on parallel shafts, or they can be mounted at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears or shafts with appropriate bearings.
In summary, there is a wide range of sizes and configurations available for spur gears, including different pitch diameters, module sizes, number of teeth, pressure angles, profile shifts, hub configurations, materials, coatings, and mounting orientations. The selection of the appropriate size and configuration depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, load capacity, space constraints, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-04-30