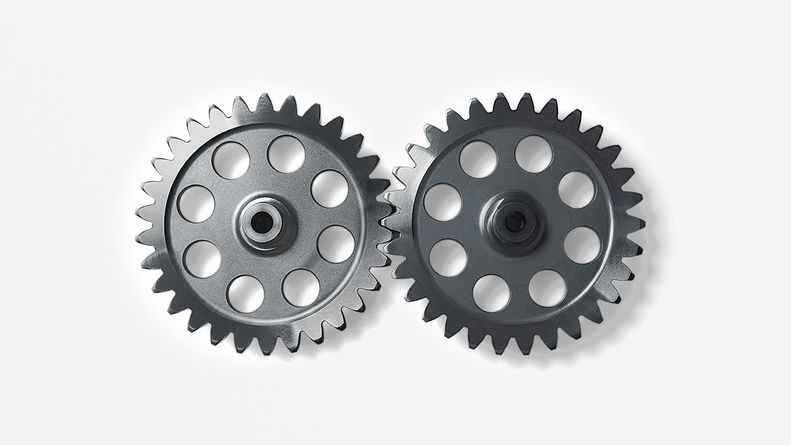
Product Description
Customize Non Standard Steel Aluminum Stainless Steel Iron Copper Alloy Gears
Non standard gears are relative to standard gears, and their design, manufacturing, and application do not follow national or industry standards. The modulus, pressure angle, tooth top height coefficient, backlash coefficient, and root fillet radius coefficient of standard gears are clearly defined, while non-standard gears may have different parameters.
Non standard gears are typically used in specific mechanical equipment or products to meet specific transmission or functional requirements. Due to the particularity of non-standard gears, their design, manufacturing, and testing processes may require more customization and professionalism.
When selecting and using non-standard gears, it is necessary to fully consider their performance, reliability, lifespan, and compatibility with other components. At the same time, in order to ensure the quality and performance of non-standard gears, it is necessary to choose gear manufacturers or suppliers with professional capabilities and experience for cooperation.
Common gear materials include carbon steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, cast iron, and copper alloy. Here is a brief introduction to these materials:
Carbon steel: Carbon steel is 1 of the most common gear materials, with high strength and hardness, and relatively low price. Carbon steel can achieve appropriate hardness and improve its wear resistance through heat treatment. However, carbon steel has lower corrosion resistance and is prone to rusting in humid or corrosive environments.
Aluminum alloy: Aluminum alloy gears have a lighter weight and good thermal conductivity, which can improve transmission efficiency. In addition, aluminum alloys also have good corrosion resistance and reliable durability.
Stainless steel: Stainless steel is an alloy material with good corrosion resistance, commonly used in gear manufacturing that requires high corrosion resistance. Stainless steel has high strength and hardness, and its mechanical properties can be further improved through heat treatment.
Cast iron: Cast iron is a commonly used gear material with high strength and hardness, and is relatively inexpensive. Cast iron gears can further improve their hardness and wear resistance through heat treatment.
Copper alloy: Copper alloy gears have good thermal conductivity and wear resistance, and have good impact resistance in high-speed and high load environments. In addition, copper alloys have high strength and hardness, making them suitable for various working conditions.
The process of customizing gears involves multiple key steps and parameter considerations, as follows:
Determine gear type: Firstly, it is necessary to clarify whether the gear is spur or helical. Straight tooth gears have strong load-bearing capacity and can withstand large torques, but may produce significant noise during high-speed operation. Helical gears have the characteristics of high overlap, smooth transmission, and low noise, making them more suitable for high-speed operation, but may generate axial force.
Determine modulus and number of teeth: modulus and number of teeth are 2 important parameters in gear design. Under the same number of teeth, the larger the modulus, the larger the size of the gear. Similarly, under the same modulus, the more teeth there are, the larger the size of the gear. When selecting, it is necessary to determine the appropriate gear size based on the load situation.
Determine gear accuracy: The accuracy of a gear has a significant impact on its performance and lifespan. Normally, the unified accuracy of gears is level 6, but specific accuracy requirements need to be determined based on actual application scenarios.
Determine aperture size and tolerance: The aperture size and tolerance of gears are also important parameters to consider in the customization process. If the gear needs to be installed in conjunction with the shaft, the size and tolerance of the shaft need to be provided. Meanwhile, different installation methods (such as top thread installation or hot fitting) can also affect the tolerances between the hole shafts.
Consider other parameters: In addition to the basic parameters mentioned above, it may also be necessary to determine other parameters based on specific output methods and design requirements, such as parameters for special situations such as flange output and hollow shaft output.
Design drawings and sample confirmation: Based on the determined parameters and design requirements, draw the design drawings of the gears and make samples for actual testing. Ensure that the customized gears meet the actual usage requirements through testing and verification.
| Products Name | Gears |
| Material | Steel/Aluminum/Stainless Steel/Iron/Copper/Alloy |
| Modulus | 2M/3M/5M/8M/14M/20M |
| Accuracy | Grade 8 ~Grade 6 |
| Hardness | 48~52HRC |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses.
Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula:
η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100%
Where:
η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage.
Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system.
Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system.
Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the gear affects the efficiency. Well-designed gear teeth with accurate involute profiles can minimize friction and power losses during meshing.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication between the gear teeth reduces friction, wear, and heat generation, improving gear efficiency. Insufficient or inadequate lubrication can result in increased power losses and reduced efficiency.
- Gear Material: The selection of gear material affects efficiency. Materials with low friction coefficients and good wear resistance can help minimize power losses. Higher-quality materials and specialized gear coatings can improve efficiency.
- Gear Alignment and Meshing: Proper alignment and precise meshing of the gear teeth are essential for optimal efficiency. Misalignment or incorrect gear meshing can lead to increased friction, noise, and power losses.
- Bearing Friction: The efficiency of a gear system is influenced by the friction in the bearings supporting the gear shafts. High-quality bearings with low friction characteristics can contribute to improved gear efficiency.
- Load Distribution: Uneven load distribution across the gear teeth can result in localized power losses and reduced efficiency. Proper design and gear system configuration should ensure even load distribution.
Interpreting Gear Efficiency:
The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation.
It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices.
By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.

Are spur gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Spur gears are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including those involving high-torque requirements. However, their suitability for high-torque applications depends on various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are designed to transmit power and torque between parallel shafts. They have straight teeth that engage fully, providing efficient power transfer. The suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications can be evaluated based on the following considerations:
- Load Distribution: Spur gears distribute the transmitted load over a larger contact area compared to other gear types. This characteristic allows them to handle higher torque loads effectively.
- Size and Diameter: The size and diameter of the spur gears play a crucial role in their ability to handle high torque. Larger gear diameters provide increased torque capacity due to the longer lever arm and larger contact area between the gear teeth.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for the spur gears is essential for high-torque applications. Strong and durable materials, such as hardened steel or alloy steels, are commonly used to ensure the gears can withstand the high stresses and torque loads without deformation or failure.
- Gear Design: Proper gear design considerations, such as tooth profile, module or pitch, and the number of teeth, can impact the torque-carrying capacity of spur gears. Design parameters should be optimized to ensure sufficient tooth strength and minimize the risk of tooth breakage or excessive wear.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Adequate lubrication is critical for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in high-torque spur gear applications. Regular maintenance, including lubricant replacement and gear inspections, can help identify and address any issues that may affect the gear’s torque-handling capabilities.
- Supporting Components: The overall system design, including the selection of bearings, shafts, and housing, should be considered to ensure proper support and alignment of the spur gears. Well-designed supporting components contribute to the overall torque capacity of the system.
While spur gears can handle high torque, it’s important to note that there are limitations to their torque capacity. Factors such as gear size, material strength, tooth design, and operating conditions can affect the maximum torque the gears can safely transmit without failure.
In some cases, other gear types such as helical gears or bevel gears may be more suitable for specific high-torque applications. These gears offer advantages such as increased load-carrying capacity, improved torque transfer efficiency, and reduced noise and vibration levels.
Ultimately, the suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications should be evaluated based on the specific requirements, operating conditions, and industry standards applicable to the particular application.
What are the applications of spur gears?
Spur gears find a wide range of applications in various mechanical systems due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. These gears are commonly used in numerous industries and equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of spur gears:
- Automotive Industry: Spur gears are extensively used in automobiles for power transmission applications. They are employed in gearboxes, differentials, and transmission systems to transfer torque and rotational motion between the engine, wheels, and other components.
- Machinery and Manufacturing: Spur gears are widely utilized in machinery and manufacturing equipment. They play a crucial role in conveyor systems, machine tools, printing presses, textile machinery, packaging machinery, and various other industrial applications.
- Power Generation: Spur gears are employed in power generation systems such as wind turbines, hydroelectric turbines, and steam turbines. They help convert the rotational motion of the turbine blades into electricity by transmitting power from the rotor to the generator.
- Robotics and Automation: Spur gears are commonly used in robotics and automation systems. They are utilized in robotic joints, actuators, and drive systems to control motion and transmit torque accurately and efficiently.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Spur gears are found in various aerospace and aviation applications. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, engine components, flight control systems, and auxiliary power units (APUs) to transmit power and control movement.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Spur gears have applications in the marine and shipbuilding industry. They are used in propulsion systems, winches, steering mechanisms, and other equipment that require torque transmission and speed control.
- Appliances and Household Equipment: Spur gears are present in numerous household appliances and equipment. They are found in washing machines, dishwashers, mixers, food processors, garage door openers, and many other appliances that require rotational motion and power transmission.
- Power Tools: Spur gears are utilized in power tools such as drills, saws, grinders, and sanders. They help transmit power from the motor to the tool’s cutting or grinding components, enabling efficient operation.
- Medical Equipment: Spur gears are used in various medical devices and equipment. They can be found in imaging systems, surgical robots, medical pumps, and other applications that require precise motion control and torque transmission.
- Clocks and Watches: Spur gears are an essential component in mechanical clocks and watches. They are responsible for accurate timekeeping by transferring rotational motion from the mainspring or oscillator to the hour, minute, and second hands.
These are just a few examples of the broad range of applications where spur gears are utilized. Their simplicity, reliability, and ability to transmit power and motion efficiently make them a popular choice in various industries and equipment.


editor by Dream 2024-05-03